Meiosis Stages Pmat 2 | Stag/sa proteins are specific cohesin complex subunits that maintain sister chromatid cohesion in mitosis and meiosis. The stages of mitosis are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, sometimes followed by cytokinesis. There are six stages within each of the divisions, namely prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis. In its first step meiosis i it's a reduction division where the a cell in the testes or the ovary divide into two each cell has half the number of chromosomes (in humans the number of. This is the final stage of meiosis i.
At the beginning of the first meiotic division, the nucleus of the dividing cell starts to increase in size by absorbing the water from the cytoplasm, and the nuclear. If you don't understand the various steps of meiosis, you will after you read this! There are two stages or phases of meiosis: The following are descriptions of the two divisions, and the various phases, or stages of each meiosis. Here we investigate the key differences and similarities between the two processes.
Each of the two meiotic divisions is divided into meiosis 1 phases. Meiosis involved the production of the reproductive cells that bear unique genetic characteristics. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: At the level of the genes, sexual reproduction is focused on the fusion of the paternal and maternal genes that result in a new combination of genes. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. Meiosis occurs in two distinct phases: Two successive divisions without any dna replication. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i & meiosis ii. • each of the meiosis ii stages are running in 2 cells at the same time. Here we investigate the key differences and similarities between the two processes. Chromosomal crossover in meiosis i. Chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs. Meiosis is like mitosis twice!
Meiosis is a very important step that prepare gametes (eggs and sperm) for participating in sexual reproduction. Meiosis is a kind of specialized cell division that occurs only in germ cells produced in the gonads of eukaryotes. Meiosis 2 results in separation the sister chromatids and for this reason, it is known as equatorial division. The following are descriptions of the two divisions, and the various phases, or stages of each meiosis. It includes two consecutive divisions and beings the total chromosome number to 23 whole creating four daughter cells.
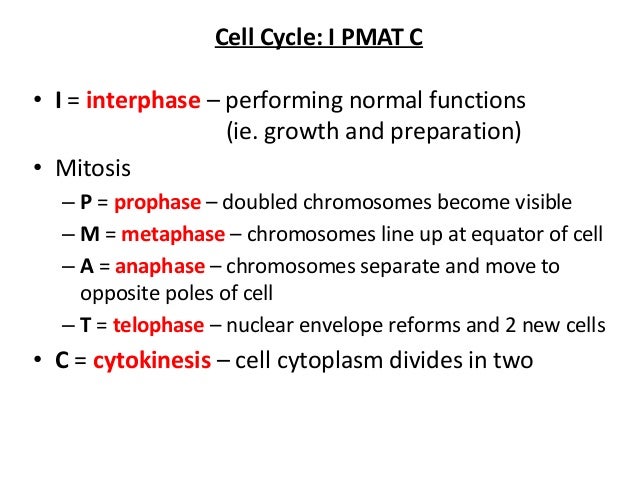
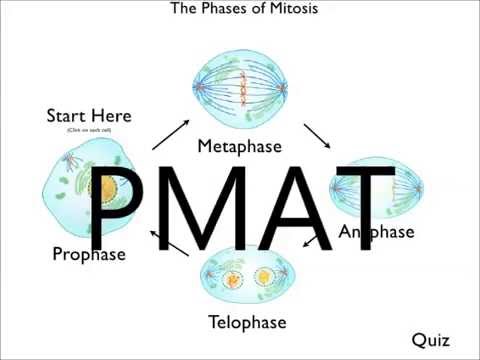
The names of these stages can be memorised by the phrase pmat. Two successive divisions without any dna replication. One of the most important processes in this stage is chromosomal replication in which each chromosome. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: Formation of chiasmata and crossing over. These are arranged in pairs, with one copy of each chromosome from mum, and the other from dad. After meiosis i, the cell enters into the stage called interkinesis. Twostages, meiosis1andmeiosis 2.eachstageiscomposed offourphases,prophase, metaphase,anaphaseandthe. • each of the meiosis ii stages are running in 2 cells at the same time. 6 stages of meiosis, continued meiosis i in anaphase i, the homologous chromosomes separate. Meiosis is the process by which gametes are made. The phases of meiosis are the same as the phases of mitosis. Meiosis can be separated into two stages
At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. Meiosis i and meiosis ii. Meiosis is a kind of specialized cell division that occurs only in germ cells produced in the gonads of eukaryotes. The essential stages that take place during meiosis are. The stages of mitosis are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, sometimes followed by cytokinesis.
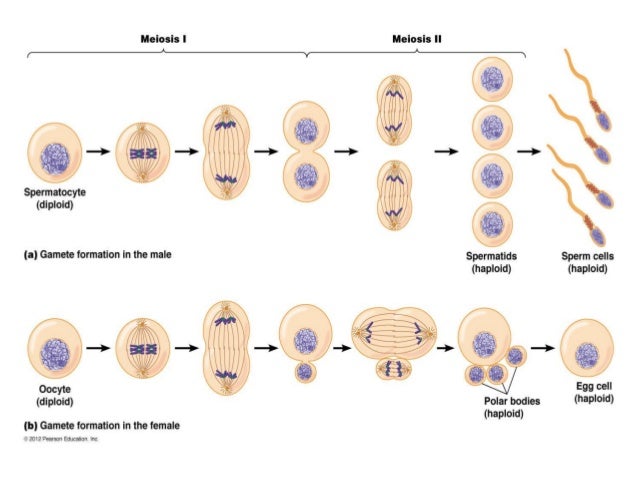
The essential stages that take place during meiosis are. It includes two consecutive divisions and beings the total chromosome number to 23 whole creating four daughter cells. If you don't understand the various steps of meiosis, you will after you read this! The stages of mitosis are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, sometimes followed by cytokinesis. An animal cell with a diploid number of four (2n = 4) proceeds through the stages of meiosis to form four haploid daughter cells. Two stages occur in meiosis, each split down into several fundamental processes. After meiosis i, the cell enters into the stage called interkinesis. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: Explore what it is, stages of meiosis and importance of. Before a dividing cell enters meiosis, it undergoes a period of growth called interphase. Formation of chiasmata and crossing over. Human body cells have 46 chromosomes. Both stages of meiosis 1 and 2 consist of four phases:
During meiosis ii, the sister chromatids within the two daughter cells separate, forming four new haploid gametes pmat stages. Two stages occur in meiosis, each split down into several fundamental processes.
Meiosis Stages Pmat 2: Interphase 1, prophase 1, metaphase 1, anaphase 1, telophase 1, prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, and telophase 2.
Post a Comment